Simulation of 1D diffraction pattern
diffraction.RdAnalytic Fourier transform of electron density corresponding to
an array of Ncell unit cells calculated using numerical
integration with the trapezoid rule. The diffraction peaks' height is
proportional to the number of unit cells ( Ncell). The
number of diffraction peaks included in the 1D diffraction pattern is
related to the maximum resolution D provided in the input.
The number of grid points for both the simulated electron density and
the resulting diffraction pattern can also be provided as input. A
further input parameter is the radius of the beamstop disc to stop
diffraction close to the incoming beam (as the resulting intensity far
outweigh the rest of the diffracted intensities).
Arguments
- sdata
A named list, normally obtained through the use of functions
read_xorstandardise_sdata. The list names correspond to different object types:a. Real numeric. The size of the unit cell.
SG. Character string. Space group symbol; either "P1" or "P-1"
x0. Vector of real numerics indicating the expanded atomic positions in the unit cell.
Z. Vector of integers indicating the expanded atomic numbers for all atoms in the unit cell.
B. Vector of real numerics indicating the expanded B factors for all atoms in the unit cell.
occ. Vector of real numerics indicating the expanded occupancies for all atoms in the unit cell.
- D
Real numeric. Maximum resolution in angstroms.
- Ncell
Positive integer. It is the number of unit cells in the 1D crystal. The default value is
Ncell=10.- N
Positive integer indicating the number of grid points for the electron density. The default value is
N=1000.- n
Positive integer determining the reciprocal space grid. The grid is made of
2*n+1regularly-spaced points from-1/Dto1/D. The value 0 is always at the centre of the grid. The default value isn=100.- bstop
Real numeric. Is the radius of the backstop disc. Intensities at points closer to the origin than
bstopare reduced to 0. The presence of a backstop improves the contrast for all diffracted intensities because it gets rid of the overwhelming intensity corresponding to the origin of the reciprocal space. The default is not to include any backstop.
Value
A named list with two vectors of real numbers, the values of the
reciprocal space grid points (in 1/angstrom units) xstar
and the intensities Imod.
Examples
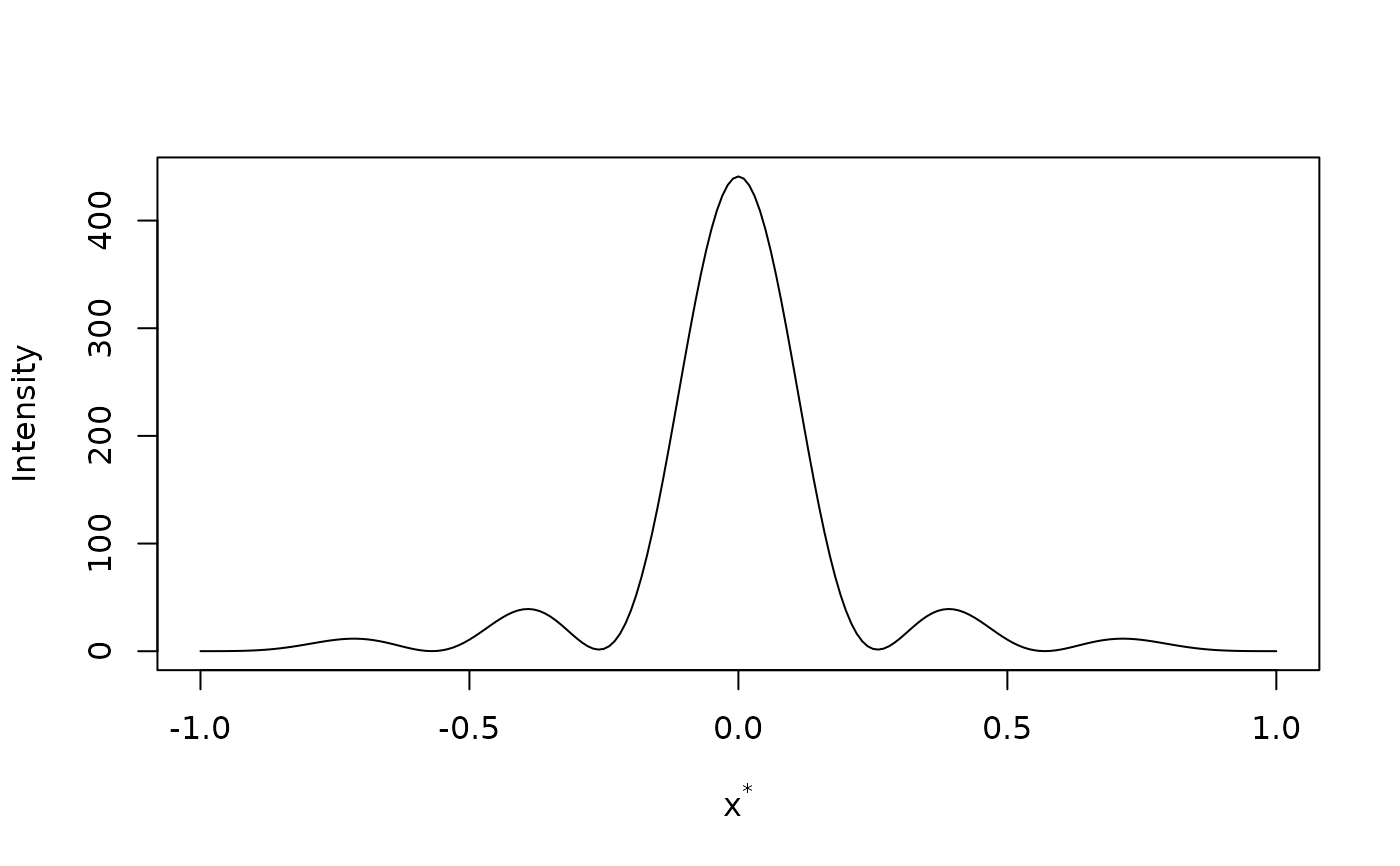
# Diffraction from just two unit cells of cyanate
sdata <- load_structure("cyanate")
# Max resolution is 1 angstroms; no backstop
ltmp <- diffraction(sdata,D=1,Ncell=1)
# Plot diffraction pattern
plot(ltmp$xstar,ltmp$Imod,type="l",
xlab=expression(paste("x"^"*")),ylab="Intensity")
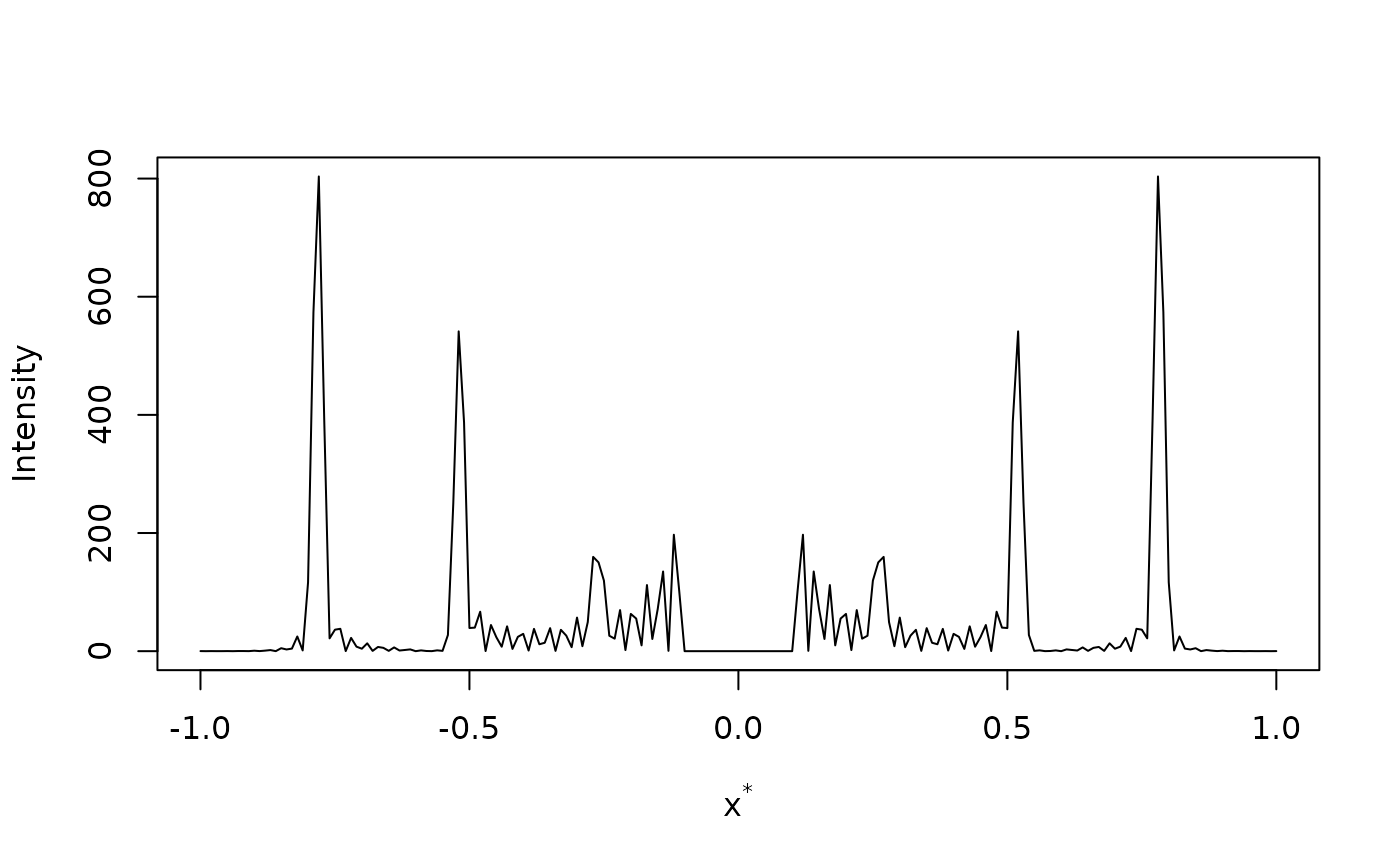
 # Diffraction from 20 unit cells with backstop of 20 angstroms diameter
ltmp <- diffraction(sdata,D=1,bstop=10)
plot(ltmp$xstar,ltmp$Imod,type="l",
xlab=expression(paste("x"^"*")),ylab="Intensity")
# Diffraction from 20 unit cells with backstop of 20 angstroms diameter
ltmp <- diffraction(sdata,D=1,bstop=10)
plot(ltmp$xstar,ltmp$Imod,type="l",
xlab=expression(paste("x"^"*")),ylab="Intensity")